As data becomes ever more distributed across multiple systems, organizations have to cope with increasingly complex ecosystems and digital business requirements.
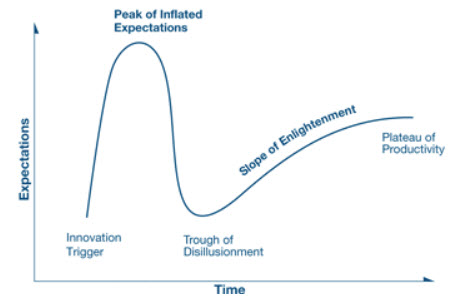
The “Hype Cycle for Data Management,” developed by Gartner, Inc. is designed to assist CIOs, chief data officers (CDOs) and other senior data analytics specialists understand the maturity of the data management technologies they are evaluating to provide a cohesive data management ecosystem in their organizations.
“This Hype Cycle will help data and analytics leaders modernize their analytics and BI programs,” says Gartner analysts and vice president, Andrew White. “The main story that emerges from it concerns the upcoming transition from visual data discovery to augmented analytics using machine learning and natural-language interfaces to augment human intelligence.”
White's primary research focus on the chief data officer role, data and analytics platforms, strategy, governance, and stewardship, along with master data management (MDM). His current role is as Vendor Lead for Oracle Corp.
“Data management continues to be central to the move toward digital business. As requirements change within the architecture of the organization and place greater demands on underlying technology, the maturity and capability of many of the technologies highlighted in the Hype Cycle will advance rapidly,” says Donald Feignberg, vice president and distinguished analyst at Gartner. “Recent years have seen many new additions to the Hype Cycle, including in-memory, cloud, data virtualization, advanced analytics, data as a service, machine learning, graph, non-relational and
Hadoop.”
Hadoop is an open-source software framework for storing data and running applications on clusters of commodity hardware. It provides massive storage for any kind of data, enormous processing power and the ability to handle virtually limitless concurrent tasks or jobs.
Two technologies are of particular interest, in that they show the impact cloud computing is having on the data management discipline. Hadoop distributions are deemed to be obsolete before reaching the Plateau of Productivity because the complexity and questionable usefulness of the entire Hadoop stack is causing many organizations to reconsider its role in their information infrastructure. Instead, organizations are looking at increasingly competitive and convenient cloud-based options with on-demand pricing and fit-for-purpose data processing options.
As part of the same cloud-led trend, SQL interfaces to cloud object stores have appeared at the Innovation Trigger stage. “We expect these interfaces to represent the future of cloud database Platform as a Service (Paas) and reach the Plateau within two to five years because they are the focus of most cloud vendors and products in this space,” said Mr. Feinberg. “They enable organizations to interact with data stored in the cloud, using a familiar SQL syntax. Object stores are well suited to storing large volumes of multistructured data, typical of data lakes.”
Of the 35 other technologies highlighted on the 2017 Hype Cycle for Data Management, four are judged to be transformational in nature. Two — event stream processing (ESP) and operational in-memory database management system (IMDBMS) — are expected to reach the Plateau of Productivity within two to five years, while both blockchain and distributed ledgers are expected to take five to 10 years.
Event Stream Processing
ESP is one of the key enablers of digital business, algorithmic business and intelligent business operations. ESP technology, including distributed stream computing platforms (DSCPs) and event processing platforms (EPPs), is maturing rapidly. Stream analytics provided by ESP software improves the quality of decision-making by presenting information that could otherwise be overlooked.
Operational In-Memory DBMS
Operational In-Memory database management systems (IMDBMS) technology is maturing and growing in acceptance, although the infrastructure required to support it remains relatively expensive. Another inhibitor to the growth of operational IMDBMS technology is the need for persistence models that support the high levels of availability required to meet transaction SLAs. Nevertheless, operational IMDBMSs for transactions have the potential to make a tremendous impact on business value by speeding up data transactions 100 to 1,000 times.
Blockchain
Blockchain
Public distributed ledgers, including blockchain, continue to have high visibility, although organizations remain cautious about the future of public (permission-less) distributed ledger concepts due to scalability, risk and governance issues. Most business use cases have yet to be proven and extreme price volatility in bitcoin persists. Presupposing the technical and business challenges of distributed ledgers can be overcome; in the short term, organizations are most likely to use distributed ledger for operational efficiency gains via the use of shared information and infrastructure. Longer term, Gartner expects a complete reformation of whole industries and commercial activity as the programmable economy develops and ledgers contribute to the monetization of new ecosystems.
Distributed Ledgers
The requirements for more standards and enterprise-scale capabilities are evolving slowly, but distributed ledgers are still not adoptable in a mission-critical at-scale context. Their value propositions, compared with existing technology, are also not clearly established, making the widespread acceptance of the technology problematic. Private distributed ledger concepts are gaining traction, because they hold the promise to transform industry operating models and overcome some of the issues of scalability, risk management and governance that plague public ledgers. As with blockchain, however, many business use cases are unproven at this time.
SC
MR


Latest Supply Chain News
- Survey reveals strategies for addressing supply chain, logistics labor shortages
- Israel, Ukraine aid package to increase pressure on aerospace and defense supply chains
- How CPG brands can deliver on supplier diversity promises
- How S&OP provides the answer to in-demand products
- AI, virtual reality is bringing experiential learning into the modern age
- More News
Latest Podcast

 Explore
Explore
Business Management News
- Survey reveals strategies for addressing supply chain, logistics labor shortages
- How CPG brands can deliver on supplier diversity promises
- How S&OP provides the answer to in-demand products
- AI, virtual reality is bringing experiential learning into the modern age
- Tips for CIOs to overcome technology talent acquisition troubles
- There is still work to do to achieve supply chain stability
- More Business Management
Latest Business Management Resources

Subscribe

Supply Chain Management Review delivers the best industry content.

Editors’ Picks